You’ve probably heard a lot about the importance of targeting keywords with your blog post.
But why should you do that? And how exactly do you target keywords?
You’ll learn how in this post.
Why Target Keywords?
If your blog content ranks well on Google, you can receive a steady stream of traffic over time.
For example, we published an article on advanced Google search operators back in 2018, and it continues to generate significant organic traffic:
Line graph illustrating the organic traffic for our advanced Google search operators post.
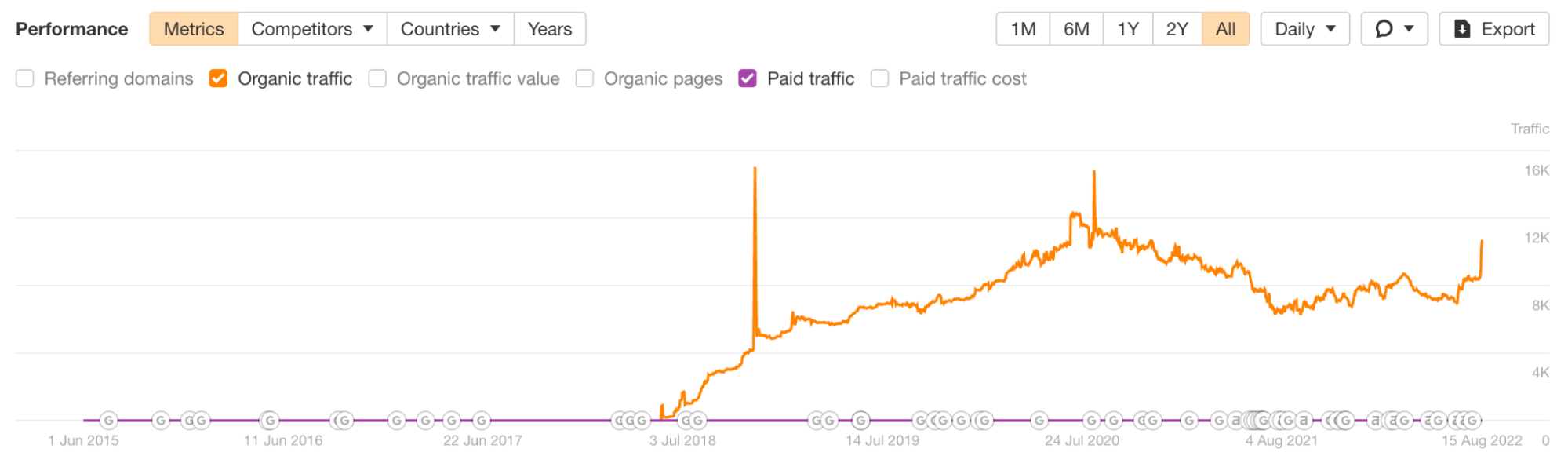
However, you can’t just publish any post and expect search traffic to start flowing in. To attract organic traffic consistently, you need to write about topics people are actively searching for.
This is why targeting keywords in your blog posts is essential.
How to Target keywords with blog posts
Now that you understand why it’s crucial to target keywords, let’s explore how to do it effectively.
1. Find keyword ideas
The first step is identifying the keywords you want to target. You’re not looking for just any keywords—you want relevant ones that people are searching for.
The simplest way to find keyword ideas is by using a keyword tool. These tools contain databases of words and phrases along with their SEO metrics. When you input a seed keyword, the tool generates a list of keyword ideas.
You can choose from various keyword research tools, many of which are free. However, free tools often come with limitations like smaller databases, limited filters, or missing SEO metrics.
To make more informed decisions, it’s better to use a professional keyword tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. Here’s how to find keyword ideas using it:
- Enter one or more relevant seed keywords. For instance, if you run a coffee blog, you could use keywords like “coffee,” “latte,” or “French press.”
- Go to the Matching Terms report.
- Switch to the Questions tab.
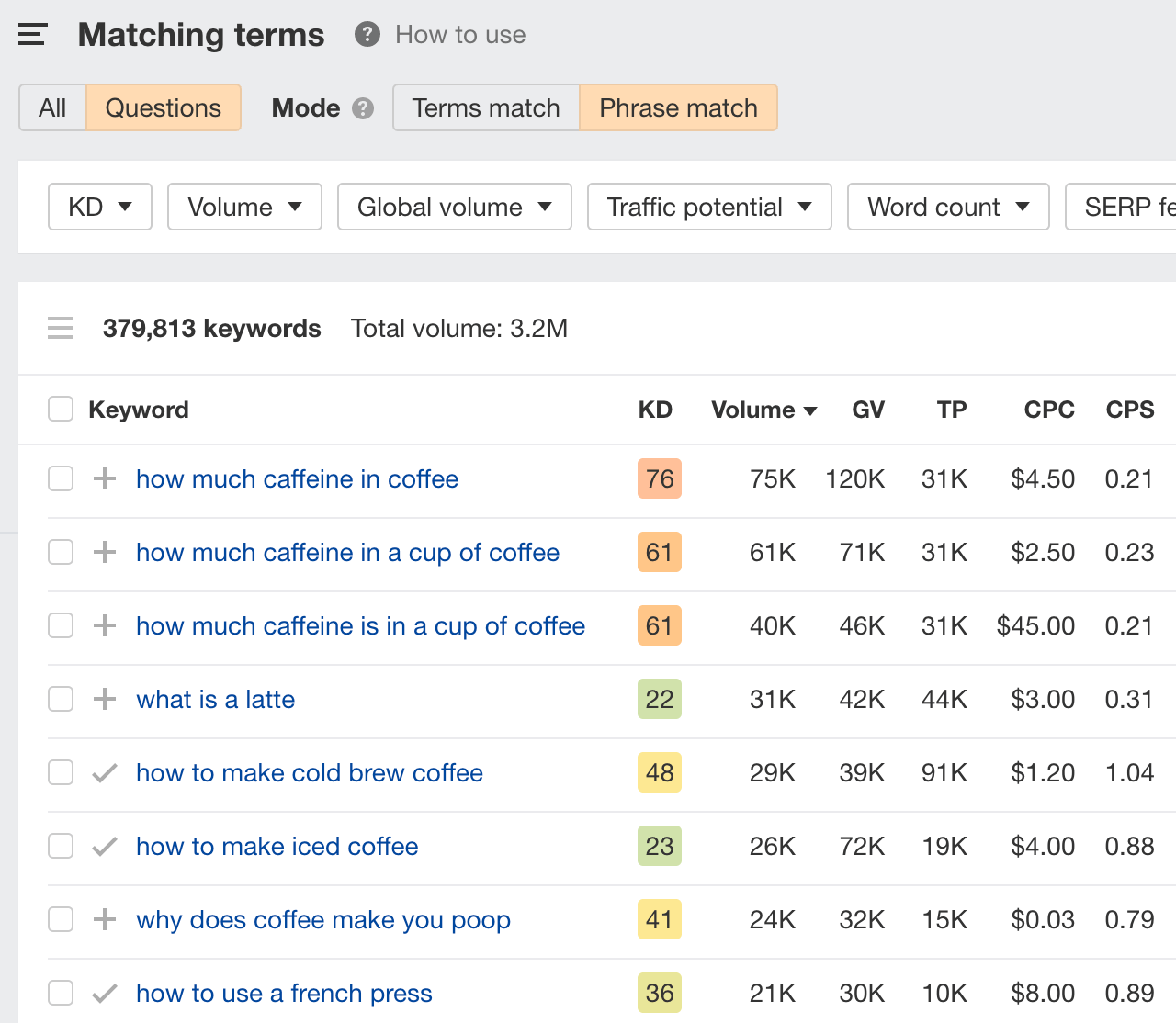
You’ll notice that there are over 300,000 potential keywords you could target. This is too many, and many of them will be too competitive. If you’re starting out, it’s better to target keywords that offer:
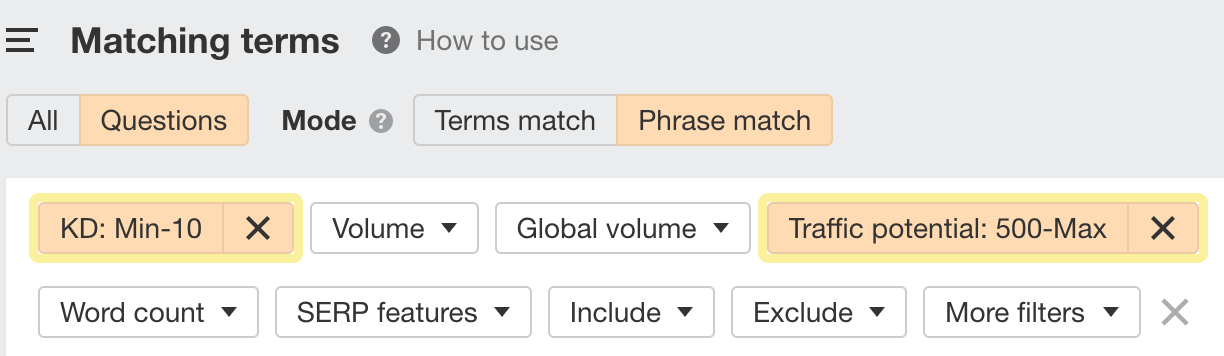
- High Traffic Potential (TP) – TP refers to the estimated search traffic you can expect if you rank #1 for a keyword. This metric is calculated by evaluating the traffic received by the current top-ranking page.
- Low Keyword Difficulty (KD) – KD indicates how challenging it is to rank within the top 10 organic search results for a specific keyword.
Use the filters available in the tool to narrow down the list of keywords:
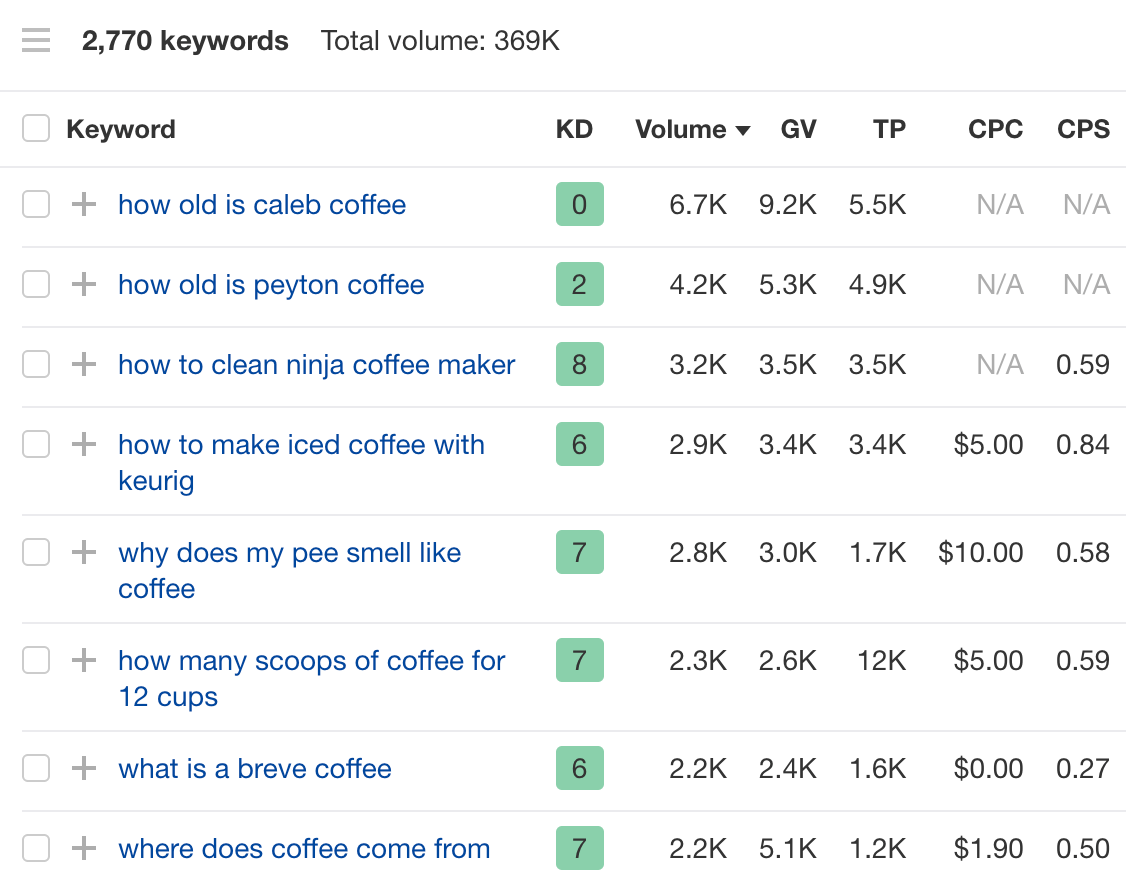
Once you’ve filtered the list, review it and select keywords relevant to your website.
2. Identify search intent
Google’s goal is to provide the most relevant content for any given query. To do this, it tries to understand the searcher’s intent behind the keyword.
To rank well on Google, you need to align your content with search intent. This can be achieved by examining the top-ranking pages for your target keyword. You want to analyze the three Cs of search intent:
- Content type – The type of content that dominates the search engine results (e.g., blog posts).
- Content format – The dominant format, such as how-to guides, listicles, or reviews.
- Content angle – The common approach or angle, like emphasizing the current year, for beginners, or using specific tools or ingredients.
For example, consider the keyword “how to clean coffee maker”:
Search engine results page (SERP) overview for “how to clean coffee maker.”
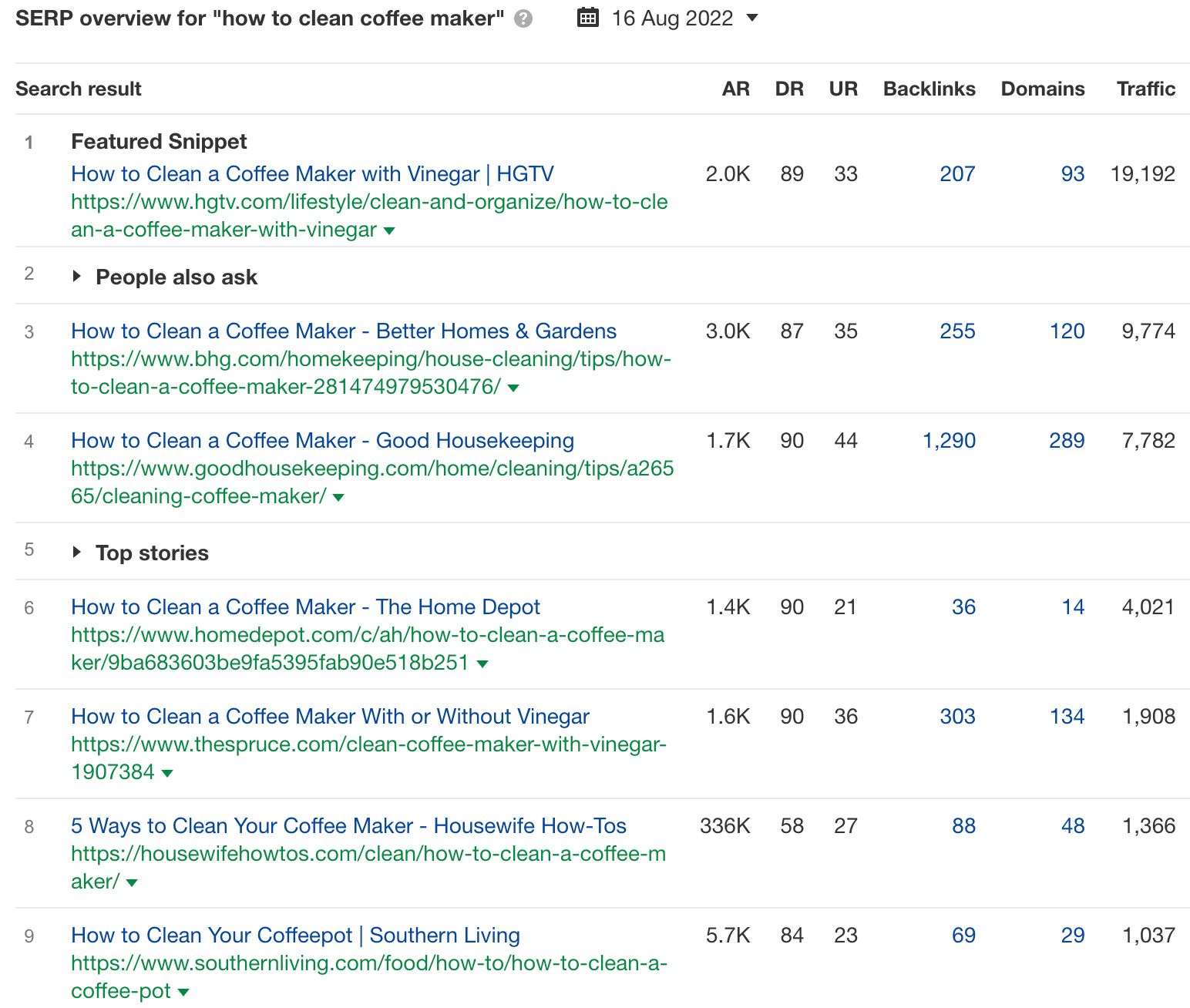
- Content angle – Many of the posts reference using vinegar, which could be an angle to focus on.
- Content type – All the results are blog posts.
- Content format – Most are how-to guides.
If you’re targeting this keyword, your best bet is to create a how-to guide on cleaning a coffee maker, possibly featuring vinegar as a cleaning method.
3. Create Your Content
Once you’ve identified your target keywords and understood the search intent, it’s time to create content that meets user expectations. Be sure to:
- Use the target keyword naturally in your content, including in headings, subheadings, and throughout the body.
- Structure your post clearly with an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
- Ensure your content provides value and solves the user’s query.
- Use images, videos, or infographics to break up the text and engage readers.
Incorporating your target keywords while delivering valuable content will improve your chances of ranking higher on Google.
4. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is targeting keywords important for blog posts?
Targeting keywords is essential because it helps your blog content rank higher on search engines like Google. By optimizing your posts around specific keywords that people are searching for, you increase the chances of attracting organic traffic, which can drive more visitors to your website.
Q2. How do I find the right keywords for my blog post?
To find the right keywords, you can use keyword research tools like Ahrefs, Google Keyword Planner, or Ubersuggest. These tools show you what people are searching for and provide metrics like search volume and competition to help you choose relevant, low-competition keywords.
Q3. What is search intent and why does it matter?
The reason behind a user’s search query is known as search intent. Understanding search intent helps you create content that matches what people are looking for, whether it’s information, a how-to guide, or a product. Aligning your content with search intent increases the chances of ranking higher on Google.
Q4. What are some free tools to help with keyword research?
Some free tools to help with keyword research include Google Keyword Planner, Ubersuggest, and AnswerThePublic. While these tools may have limitations compared to paid versions, they can still provide valuable insights into what people are searching for.
Q5. How can I naturally include keywords in my blog post?
To naturally include keywords, use them in your Headings, Subheadings, and throughout the Content. Avoid keyword stuffing and make sure the keywords fit seamlessly into your sentences. Focus on delivering value to your readers while optimizing your content for search engines.





